Business Law Chapter 1
Business Law Chapter 1 有学:
✅1.1 Describe the nature of Malaysia legal principles✅Definition of law✅Recognize the function of law✅Interpret classification of law✅Categorize sources of law in Malaysia✅1.2 Outline Malaysia judicial system✅Identify doctrine of separation of powers✅Compare the hierarchy of courts✅Explain the jurisdiction of each court✅Identify the role of judges in interpretation of statutes
1.1:Describe the nature of Malaysia legal principles
Definition of law
- Oxford English Dictionary, law is defined as ' the body of enacted(written/gazette)(mengubal) or customary rules recognized by a community as binding.'
- Sir John Salmon defines law as 'the body of principles recognized and applied by the state in the administration of justice'
- John Austin defines law as 'a commond set by superior being to an inferior being and enforced by sanctions (punishments)
Recognize function of law
- basic function of law
- advantage of law
- disadvantage of law
Classification of law
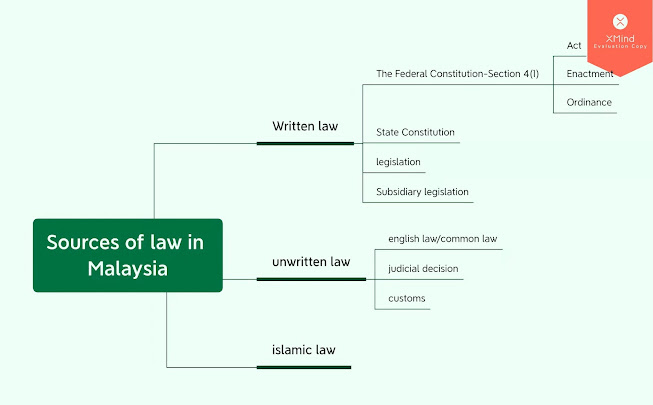
Main Sources of Malaysia law
📖written law也被称为statute law
🔎The Federal Constitution- Section 4(1) 是the supreme law of the country最高法律。
- Act 国家独立后制定的
-Enactment made by Legislative Assemblies 每个国家用的,除了sarawak
-Ordinance 是在1946年后,马来西亚独立前制定的
🔎State Constitution
-每个州有自己的法律
🔎Legislation
-暂定版本的法律,有可能会变成written law的一部分
🔎Subsidiary Legislation
-perundangan subsidiari
📖unwritten law
🔎English law/common law
-not all of English's common law and rules of equity from part of Malaysia law.
🔎Judicial Decision法官判决
-comprise Res judicata 判决书
-comprise ratio decidendi 判决理由
-comprise obiter dictum 服从判决
🔎Customs
-family law 用来处理小case 种族纠纷或者家庭纠纷
-马来西亚的customary law是 the Adat Pepatih 和 the Adat Temenggung
📖islamic law
-顾名思义,islamic law是给islam人的法律
-Syariah Court管理
-一般上用来处理财产分割或者离婚案件
1.2 Outline Malaysia judicial system
Identify doctrine of seperation of power
Compare the hierarchy of court
Explain the jurisdiction of each court
👀 Subordinate Court
⚡Penghulu's court
-最低的court
-用来处理不超过rm50的民事案件
-用来处理不超过rm25的刑事案件
-马来西亚半岛的法律 (不包括沙巴和砂砬越)
⚡Native Courts
-这个是沙巴和砂砬越的法律
-用来处理不超过rm50的民事案件(不包括土地)
-处理违反的native/custom law
⚡Megistrates Court
-处理一些比较小的民事和刑事案件
-magistrates court 分成first class 和 second class
⚡Session Court
-最高的subordinate court
-刑事案件可以判除了死刑以外的刑罚
-民事案件可以处理不超过rm100,000
-一般上不处理土地,信托的案件
👀Superior Court
⚡High Court
-有比session和magistrate高的权力
-处理sesion和magistrate无法处理的case
-处理破产,土地,信托等案件
⚡Court of Appeal
-judges一定要单位数 (避免出现平票的局势)
-处理至少要claim rm250,000以上的case
-对high court的裁决不满,可以上述,把case带到Court of Appeal
-关庭后,不能重开,重听,重判
-没有权利重新审视案件
⚡Federal Court
-马来西亚最高的court
-处理民事或刑事case (不满court of appeal的判决)
-有关YDPA的case
-YDPA=Yang di-Pertuan Agong 马来西亚最高元首
-不是随便可以把case带到federal court的
EXTRA:
Juvenile Court 是用来处理少于18岁的刑事案件。不能判死刑。如果罪犯感到内疚,会被送到感化院接受教育。
Identify the role of judges in interpretation of statutes
🍀The Literal Rule
-根据字面意思判决
🍀The Golden Rule
-根据字面意思会显得荒谬,有其他意思代替
🍀The Mischief Rule
-express the intention of the Act of Parliament




没有评论:
发表评论